Machine Learning
A computer is said to learn from experience E with respect to some class of tasks T and performance measure P if it’s performance at tasks in T, as measured by P, improves with experience E
Definition:- Machine Learning is all about learning with data, it’s used to find out the pattern in data on input and output variables and when it find out the pattern, we provide it with new data to our machine learning algorithm and it try to find out the predicted output for that new given data
Life cycle of typical machine Learning problem.
Specify business problem and requirement.
Data will be collected by multiple sources, majorly by researchers.
Data Cleaning ( Filling missing data, Smoothing noisy data), Data transformation ( Normalization or feature Scaling), Dimensionality Reduction ( Removing unwanted features)
Graphical Representation of data like pie chart, graphs, histograms etc. To find out relationship between data ( X & Y values )
Types of Machine Learning
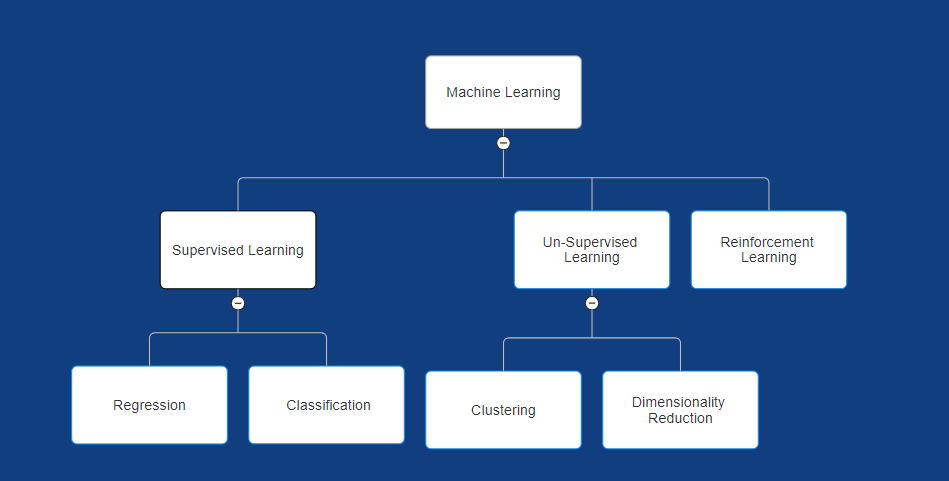
In supervised learning machine knows something beforehand means, We have already have data with features and labels present in it. We train the model with data itself and thing we want to know that with new data as input form of similar kind whether our model is able to make right prediction or not.
For example, suppose our model is trained with the images of apple and it able to identify all the features of apple. Now we want to see by providing it with new unlabeled-images of apple our model able to tell us that it’s an apple or not.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.